Our topics
Business Analytics
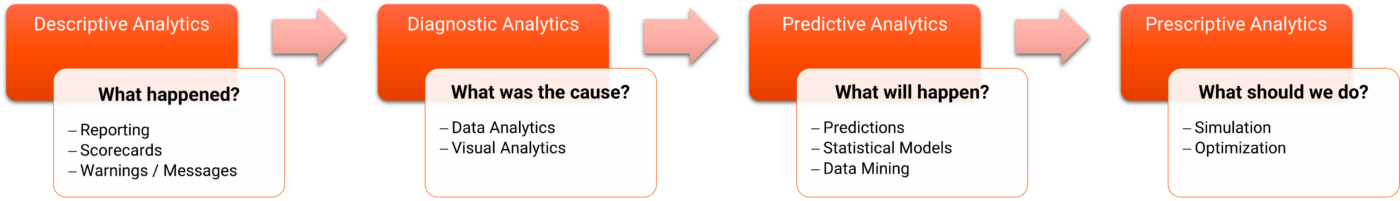
Business analytics refers to the practice of utilizing data, statistical models, and quantitative techniques to derive insights and make informed decisions within a business context. It involves collecting, organizing, and analyzing data to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships that can drive strategic actions and optimize business performance. By harnessing the power of data, business analytics enables organizations to gain a competitive edge, improve operational efficiency, and make data-driven decisions to achieve their goals.
Big Data Analytics
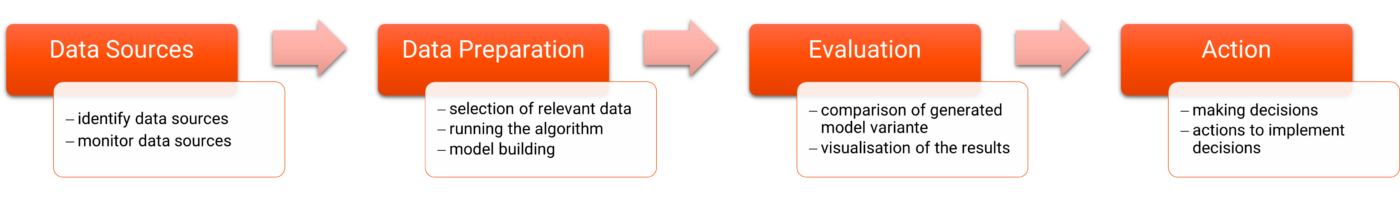
Big data analytics refers to the process of extracting meaningful insights and patterns from large and complex datasets, commonly known as big data. It involves the use of advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning, data mining, and predictive modeling, to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and trends within massive volumes of structured and unstructured data. Big data analytics enables organizations to make data-driven decisions, gain valuable insights, and discover new business opportunities that were previously inaccessible or challenging to uncover with traditional data analysis methods.
Process management
Process management refers to the systematic approach of designing, controlling, and improving business processes within an organization. It involves identifying, mapping, and documenting processes, defining process goals and objectives, and establishing performance metrics to measure process effectiveness. Process management aims to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and ensure consistent delivery of products or services by optimizing processes, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing process improvements.
Production controlling
Production controlling, also known as manufacturing or production control, is a management process that focuses on planning, monitoring and controlling production activities within an organisation. It involves the monitoring of the entire production process to ensure that it meets pre-defined goals, objectives and standards. Production controlling includes activities such as production planning, scheduling, inventory management, quality control and performance measurement, with the aim of optimising resources, minimising costs and maximising production efficiency.
Discrete-event simulation
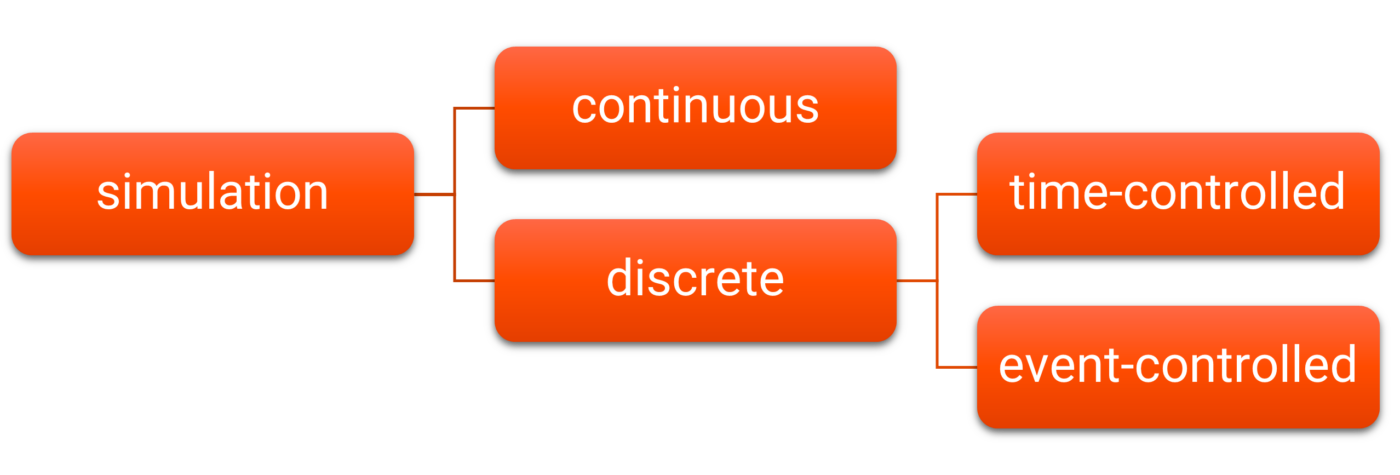
Discrete-event simulation is a modeling technique used to study and analyze complex systems where events occur sequentially in discrete time intervals. It involves creating a computer-based simulation model that captures the behavior and interactions of entities within the system, such as customers in a queue or machines in a manufacturing process. By simulating the events and their impact on the system, discrete-event simulation enables decision-makers to evaluate different scenarios, optimize processes, and improve system performance without the need for real-world experimentation.
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is about incorporating digital technologies and automation into manufacturing and industrial processes. It involves the use of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), robotics and big data analytics to create smart and connected systems. Industry 4.0 aims to increase productivity, efficiency and flexibility in industry by enabling real-time data exchange, autonomous decision-making and optimisation of the entire value chain.
